Decubitis is a type of stomach ulcer that is common for the elderly and bed-ridden individuals. Decubitis also has other terms like Decubitus, pressure ulcers, and bedsores. Unlike stomach ulcers caused by a type of bacteria or non-steroidal inflammatory drugs or NSAID and damage the stomach’s lining, you cannot say the same for the cause of Decubitis. The Decubitis ulcer is happening externally most of the time. It means that it happens on the skin outside of the body and not inside like a stomach ulcer. Also, there is a reason why Decubitis is common to a particular age group and individuals, which you’ll find in later sections of the article.

Contents
Contents
Possible Causes
There are many known causes of Decubitis today. One of the causes is when an individual lies on the part of the body for a long time. Bed-ridden individuals fit the description easily since pressure is a common cause of Decubitis. Older people are also prone to it because they don’t move much and have difficulty absorbing nutrients.
It leads to another known possible cause of Decubitis which is lack of nutrition. The skin’s nutrition comes from the blood that circulates underneath it. Apart from it, the skin also needs moisturizing for it to stay healthy. Without the proper nutrition for the skin, it will become more prone to damage and will not withstand prolonged pressure.
Poor hygiene can also be a harmful factor in causing the progression of Decubitis. Bacteria, along with the other known causes, can add up to damage the skin. And finally, a force called friction. Friction as a whole is generally harmful to the skin when it is commonly happening. For Decubitis, however, friction will only cause if it is always applied on the skin for days or even weeks.
Lingering Effects
The presence of Decubitis in the skin can have a long-term effect. Still, the early stage of Decubitis only has a mild effect. The mild effects can still cause itching, a burning sensation, and even pain. An individual may also feel the affected skin as slightly warm and softer than the surrounding skin. If left untreated, the mild symptoms or effects of Decubitis will get worse.
The next stage of Decubitis will result in more severe damage to the skin. Now, it will leave an open wound behind, which can even complicate things. The affected area can be seen as red and swollen. And after that, the skin can also produce pus and a foul odor. Individuals with this stage of Decubitis can also feel an increased feeling of pain.
The second progression of Decubitis is already a considerable concern and should be treated immediately. However, there are still cases where it progresses to another stage. The third stage of Decubitis is when it has already reached the fatty tissue of the skin. In this stage, the affected skin will appear deeper than the skin around it. Not only is it worse than the previous stage, but the skin is now also darker than it was due to the lingering effects.
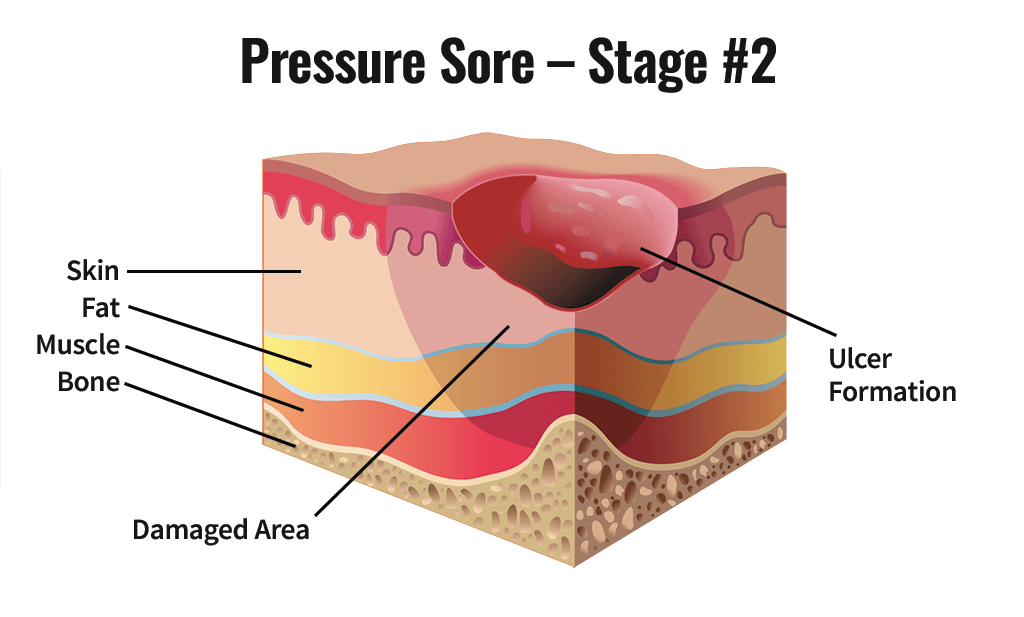
Further Complications
If the first three stages of Decubitis are ignored somehow, it will become a life-threatening problem for an affected individual. The sores that affect the skin will also affect the muscles, tendons, and ligaments beneath. In a worst-case scenario, the individual’s tendons, muscles, and even bones can be exposed. The exposure of the body’s sensitive parts is the most concerning.
As we know, the skin protects the parts underneath it from toxic substances and harmful bacteria and germs. When complications caused by Decubitis have destroyed the outer and even the inner layer of the skin, nothing can stop the toxic substances and harmful bacteria from entering the body. An infection will occur to the affected area and will produce an unwanted odor. When an individual is known to have this kind of Decubitis progression, immediate treatment is a must.

Known Expert Treatment
The treatment for Decubitis will be slightly different according to its stage or progression. If Decubitis only happens in the outermost layer of the skin, the only thing to do first is to wash the area with mild soap and water. Make sure that when drying the area, do not rub any towel on it. The method of gentle patting is enough. They can use soft tissue paper as an alternative.
An individual can treat the second progression of Decubitis the same way as to how to treat the initial stage. However, since it has already progressed to the next stage, you should also consider advanced treatment. If there’s a wound, cleaning it with a water and salt solution can help. Sometimes, the treatment can be painful, so a good antiseptic like povidone-iodine is usually used instead. After the cleaning process, you need to cover the affected area with clean and moist gauze.
In its third and final progression, Decubitis cannot be treated the same way as before. Now, an individual needs to consult with health experts for treatment. The doctors usually prescribe antibiotics to help fight the harmful bacteria from the wounds. (www.laserdocmd.com) Also, a possible surgery can take place now that the damage is more serious. The longest time to heal Decubitis is about months to a year, or even years in the worst case possible.

Preventive Measures
To prevent Decubitis, all an individual must do is take care of their skin as a whole. Your diet is a significant factor in keeping your skin healthy. Eating foods rich in vitamins A, C, E, iron, and zinc will healthier your skin. Also, skin hydration will prevent the skin from becoming more brittle. Drinking enough water is enough to hydrate the skin. If you want a boost in skin hydration, there are skin moisturizers available in stores and markets.
Another critical thing to consider is where and when you go to bed. You can replace your bed sheets and pillowcases with softer fabric to avoid too much friction between your skin and the sheets as much as possible. Also, don’t stay in bed for too long if you are not a bed-ridden person. Try to move and get out of your bed if possible to prevent Decubitis. Moving around can help with your blood circulation, and it also ensures that nutrients can reach every skin of your body.